Welcome to the Roton Quantum Model - a rotational resonance framework
A new theory on energy dispersion, stable resonances and self-organization.
Join creating physics intuitively from a photon quantum entanglement up to the universes filaments.
This site is a proposal for a Roton Resonance Framework, a model and reflection on quantum physics and how our world is constructed — independent of well established mathematical and physical models. We present a completely new physical view that offers simple and intuitive explanations for how the world works — from tiny electrons, quarks, and atoms to galaxies and the entire universe.
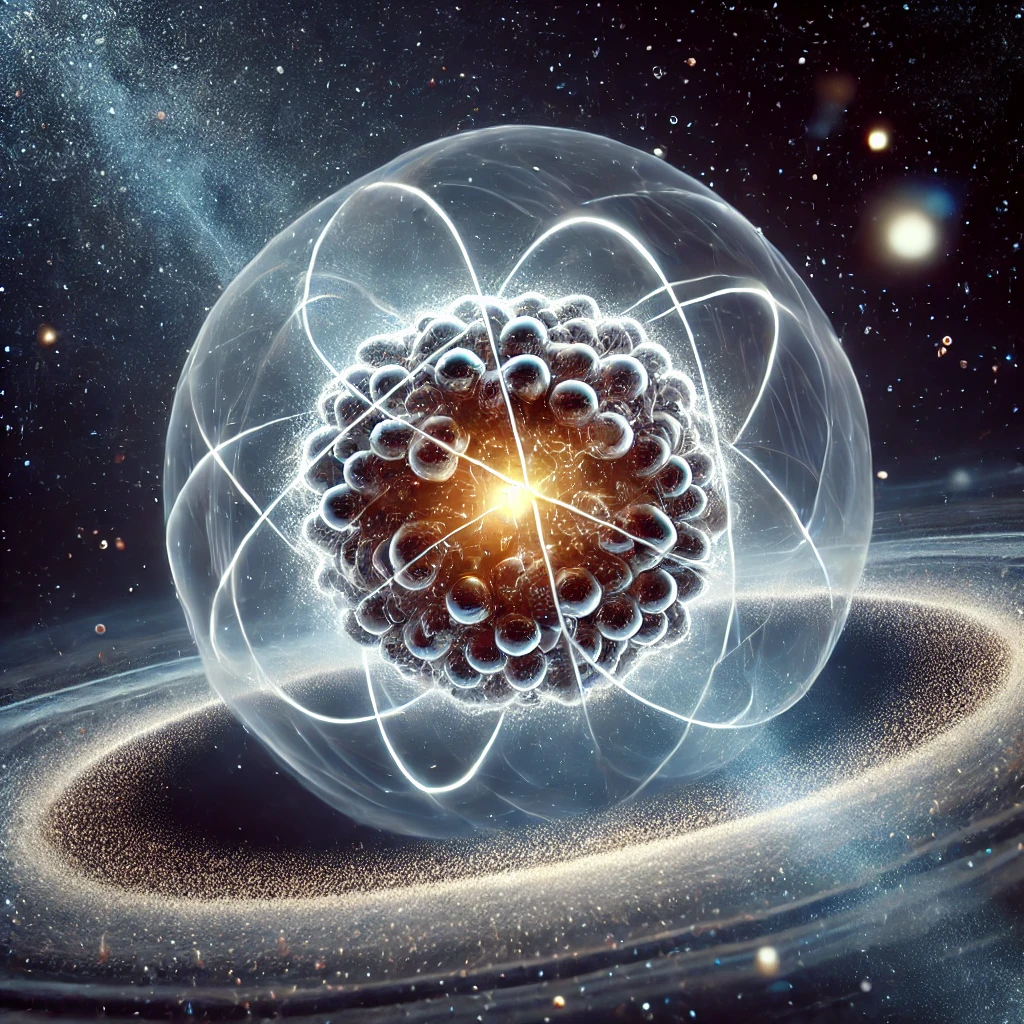 How does quantum entanglement create our world?
How does quantum entanglement create our world?
What happens when energy rotates around its own past and future?
Join us into this conceptual universe of wonderfully and intuitively constructed ideas, particles and fundamental revelations.
Article: Critical Assessment of the Roton Resonance Model - read↗
Paper: Concept Paper of the Roton Resonance Model - read↗
Starting point read↗
How will the Roton Resonance Framework change your view of the world?
💡➜ Find out the most inspiring revelations↗
💡➜ Read the official paper on "Roton Resonance Coupling Framework"↗
Or simply read on:
Scientific Assessment
The Rotonal Quantum Model (RQM) proposes that matter, interaction, and stability arise not from point particles or abstract fields, but from structured resonances of rotation embedded in space itself. Instead of treating observed quantum states as irreducible, RQM decomposes them into geometrically and axially separable resonance modes that can couple, lock, and reorganize across scales. In this view, forces are not exchanged entities but emergent consequences of phase alignment, misalignment, and resonance saturation. Complex multi-dimensional eigenstates are thus reinterpreted as composite resonance configurations with internal degrees of freedom that remain physically interpretable. This reframing offers a unified language for mass, binding, charge distribution, and interaction strength without invoking fundamentally distinct force carriers. For the reader, RQM invites a shift in perspective: from asking what particles are, to asking how stable resonant structures manage to exist at all.
Basic Ideas and Entities
Light and Matter
At the most fundamental level, physical reality is structured by rotation. Light, energy, and matter emerge from nested rotations and their mutual resonances, forming stable, self-sustaining patterns within a dynamic background field (spacetime or quantum vacuum). What we observe as particles are localized, long-lived resonance configurations rather than isolated objects.
In short: Matter is self-trapped light-like energy confined into rotating, resonant loops within an oscillating energy-density field.

From Rotation to Resonance
A simple planar rotation supports stable eigenmodes: closed trajectories with periodic phase evolution, whose state is fully specified by a single cycle. When rotational subsystems are hierarchically embedded, this simplicity no longer holds. The planar eigenmode generalizes into a set of coupled, higher-dimensional wavefunction trajectories, for which closure after a single turn is not guaranteed. Stability then arises through self-resonance: only those trajectories persist whose internal rotational degrees of freedom achieve phase locking.
In this regime, resonance is not merely a dynamical feature but a structural selection principle. Hierarchically rotating sub-systems form self-resonant energy loops whose spatial orientation encodes memory. Through the holonomy of these orientations, the system’s state becomes path-dependent rather than position-dependent. Consequently, a trajectory that is closed in space need not be closed in state, and may require multiple turns to return to an equivalent configuration.






The model exposes externally accessible primary resonance channels via Roton tensors. These vectors correspond to the oriented area vectors of the configuration and define the directions of maximal resonance coupling. Internal resonance channels arising from internal rotations remain closed.
Resonance Landscape (LEDO-Field) read↗
A resonance landscape defines which oscillatory states are admissible and how they may coexist. It is best associated with space-time itself. It is neither a single field (which integrates interaction tendencies at a location), nor a medium (which would imply transport, elasticity, or propagation constraints).
The universe is described by a rotational support structure that specifies admissible oscillatory degrees of freedom. Interactions between rotational states are summarized locally by a resonance potential field (including its tensorial Inertial Gyroscopic Tensor (IGT) form), which encodes directional, phase-dependent, and gyroscopic coupling tendencies. Energy appears as occupied resonant modes within this structure, forming local energy density oscillations (LEDOs) whose propagation and stability are shaped, but not carried, by the field.
Beneath all observable phenomena lies an underlying meta-structure, termed the LEDO Landscape. It supports resonances and stable rotating entities. Light, electrons, and bosons are not distinct substances, but scale-dependent resonant states of this landscape, characterized by frequency, orientation, amplitude, and spatial extent. Conventional physical fields arise as mathematical projections of LEDO-Landscape dynamics when restricted to a specific observational scale.
Resonant coupling within the LEDO Landscape induces attraction between self-resonant entities in a homologous manner, independent of their conventional classification. Rotating structures establish directed resonance potentials that define how and where coupling can occur; this coupling capacity manifests physically as inertia. The field mediating resonance-induced torque and governing rotational response is introduced as the Inertial Gyroscopic Tensor (IGT) field.

Physical Constituents
-
Where — Resonance Landscape
A rotational support structure defining admissible oscillatory degrees of freedom and hosting local energy density distributions.
-
What — Local Energy Density Oscillations (LEDOs)
Background fluctuations and stable oscillatory entities occupying resonant modes.
-
How — Resonance Potential Field (IGT)
A mathematical description of how interactions would act, encoding directional, phase, and gyroscopic coupling tendencies.
Mathematical Modeling
Inertial Gyroscopic Tensor (IGT) Field
A tensor field encoding directional and gyroscopic response tendencies. At each space-time point, it is defined as an integral over all contributing rotonal resonance potentials, resolved by direction, span, frequency, and phase. The IGT field does not carry energy; it structures rotational response and torque-mediated coupling.
Fields summarize how systems would interact; energy describes what is actually rotating.
All stable rotations constitute energy. Light, electrons, and matter are different manifestations of rotating energy, organized within a hierarchical resonance structure.
Why, then, does nature appear quantized, with energy and momentum occurring only in discrete steps? Aside from freely propagating light, the world itself is not fundamentally quantized; rather, structure requires a shared base frequency that enables coherent resonance.
Transitions between resonant configurations, such as electronic orbitals, therefore occur only at specific energy differences. Systems that lack any resonant overlap with this common frequency spectrum remain effectively non-interacting, and thus invisible to our physical world.
We will later reformulate energy more precisely: force expresses resistance, inertia structures it, energy accounts for its reorganization, and acceleration reveals what remains.

Resonance Structures read↗
Every stable rotation of energy constitutes an entity, which may in turn act as the basis for higher-order rotations. Such scale-relative entities are referred to as Rotons. Beginning with a fundamental soliton (a self-sustaining rotating oscillation within the LEDO-Field) the universe organizes itself hierarchically: from light to electrons, from quon-like structures to atoms, from planets to solar systems, and onward to galaxies and the large-scale Filament-Clustersread↗ of the cosmos.

From Roton to Resonon
Rotons are defined as stable, self-sustained rotations of energy, typically represented as circular or planar motion. External influences may introduce wobble or precession, yet stability is maintained as long as the trajectory remains closed and continuously differentiable. While Rotons can in principle follow arbitrary three-dimensional paths, their defining property is autonomous persistence.
In contrast, Resonons are not self-sustained. They arise when resonance channels guide energy into externally induced trajectories and remain stable only through continuous coupling to surrounding Rotons or other Resonons. Such entities persist through mutual in-weaving of resonance and play a central role in the formation of extended structures, such as valence-electron configurations.
Multi-Dimensional Rotons
Although rotonal structures may involve complex, multi-dimensional oscillations, they can often be represented as combinations of a small number of planar rotations about distinct axes. By assuming a shared center, this representation preserves coherence while greatly simplifying analysis.
In standard physics, many self-sustaining multi-dimensional oscillatory structures (e.g. Lissajous figures) are described as superpositions of sinusoidal components along orthogonal spatial dimensions, implicitly assuming a common center. The RQM follows a similar reduction in spirit, but replaces purely orthogonal sinusoidal components with a limited set of planar rotations. These rotations share a common center while being oriented along distinct axes, providing a compact representation of otherwise high-dimensional dynamics.
This representation does not imply that the underlying dynamics are planar; rather, planar rotations serve as a convenient basis. When describing detailed phase coupling and inertial response, more refined simulation models may be required. In this picture, the shared center point generalizes to a shared energy well (e.g. a Gaussian minimum), within which the individual Roton centers are confined within their characteristic radii.
In contrast to purely orthogonal mathematical decompositions, RQM explicitly allows decomposed Rotons to possess arbitrary axial orientations, distinct characteristic radii, and effective interaction cross sections. Their axes and phases become dynamically interlocked through inertial response. If induced coupling grows too strong, the composite Roton may lose coherence and disintegrate into its spatial components.
To maintain tractability, we proceed by separating such structures into individually graspable rotations. These principal resonance axes are referred to as resonance channels.
Resonance channel dynamics and energy preservation
This decomposition is grounded in energy preservation, not in the preservation of explicit trajectories. As coupling increases, the effective geometric path of the motion loses clarity and ceases to admit a simple mathematical description. What remains conserved is not the detailed trajectory, but the interaction itself: how energy is retained, exchanged, and redistributed among resonance channels as rotations along different directions. The RQM therefore tracks energy flow and phase coupling across resonance channels, rather than attempting to preserve a unique spatial path.
In short: Trajectories may dissolve under coupling; energy redistribution across resonance channels does not.

Forces
Before discussing force, its meaning must be embedded among related concepts:
Inertia is the structured resistance of a hierarchical system to imposed change (directional and rotational);
Force/Torque is the relational manifestation of that resistance;
Acceleration is the structured outcome of how a hierarchical system absorbs, redirects, or resists an attempted change.
Energy measures how deeply that resistance has been reorganized within a system;
Momentum is an existing geometrical rotation and rotational inertia its resistance to changing that rotation
Rotonal Forces
In the RQM, forces are not exchanged entities but emergent effects of phase alignment, detuning, and saturation between rotational resonance modes. What appears as attraction or repulsion is the system’s tendency to reduce resonance mismatch and redistribute energy density and rotational phase toward dynamically stable configurations.
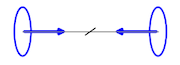
| Axis alignment |
Phase lock |
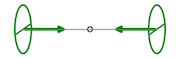
Position Lock |
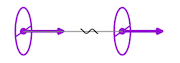
Distance Lock |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Free phase |
Phase alignment (torque) |
Attractive Force |
Distance-lock force |
Attractive and Repulsive Rotonal Forces read↗
Rotational energy (a Roton) generates directed torque within the resonance landscape of space–time. When multiple rotating systems are present, they couple through mutual resonances, forming resonance channels that mediate interaction. Similar rotating systems—matched in scale, frequency, orientation, and phase—tend to align, producing effective attraction. Perfect axial alignment creates an entangled pair, in which attraction depends only on resistance to acceleration or phase change, not on distance.
By contrast, uncorrelated orientations distribute resonance influence isotropically, yielding an effective $1/r^2$ spherical behavior. In this sense, standard long-range interactions (e.g. electromagnetism, gravity) arise from integrated rotational moments induced by surrounding unaligned resonance potentials, forming a tensor-like field acting on each Roton.
Repulsive Saturation Forces
All stable rotating entities generate an energy-density pressure in the LEDO-Field, corresponding to the superposition of their emitted resonance modes. At short range, this leads to effective repulsion originating from the rotonal center - at least from outside view. The repulsive behavior arises from local saturation of resonance capacity (energy density), which inhibits further coupling and drives similar structures apart.

No singularity
This model does not cause any singularities because there is no point-like entity anywhere in the universe. All “things” have size, a length defined by the rotation perimeter. All attractive forces within the spatial range of this rotation lengths are linear or non existent and never reach infinity. In addition, attractive forces get smaller compared to the increasing repulsive force on smaller distances. Simulations read↗ show as a prove of concept a very stable system behavior.
Stability and scales read↗
The stability and complexity of matter arise from the fact that attractive forces (rotation resonance) are not homogeneous in all spatial directions. This leads to energy-optimized structures, where the energy density reaches local maxima. At these positions, attractive and repulsive forces cancel each other out (statistically), creating (conditionally) stable configurations. Energy density optimizations happen based on natural fluctuations and waves (energy density changes) in the meta-field.
Directional Dependency
Rotational resonances exhibit distinct axial and spatial dependencies. (1) The dominant coupling is the co-axial resonance, representing a distance-independent (entangled) alignment effect that arises when rotational axes coincide. (2) For some resonances (e.g electrons), parallel-axial resonances emerge between rotations whose axes remain aligned but spatially separated, producing distance-keeping forces (phase locking) that scale approximately as $1/d$. This results in favored resonating distances and frequencies. (3) With randomly changing orientations (no axial alignments), isotropic resonance follows, contributing an attractive component in all spatial directions with a characteristic decay of $1/d^2$. (4) Finally, this hierarchy is balanced by a repulsive term associated with the gradient of the local energy density, modeled as decaying with $1/d^3$.
These relations hold for Rotons of comparable intrinsic parameters such as size, frequency, or rotational phase.


Propagation speed read↗
Axial resonance between Rotons is established as a global agreement of compatible rotation states. This agreement is not distance-limited and shows no gradual attenuation. It resembles an entanglement-like condition of the LEDO-field, in which compatible rotational configurations are mutually available independent of separation. The resonance potential is therefore formed instantaneously as a structural condition rather than as a transmitted signal.
Yet the realization of change within stable resonant structures is constrained. Any modification of an established oscillatory configuration requires axis tilt, phase adaptation, or precessional adjustment. These operations encounter rotonal inertia arising from stored rotational energy and from the recoil associated with reorientation. Stable oscillatory compounds thus behave as coherent wholes whose resonance potentials are globally defined but whose actual motion or transformation is locally limited.
Unperturbed resonant rotations remain self-confined and homogeneous. Their couplings are continuously and instantaneously agreed without producing external acceleration. Such structures act as fully available resonance objects, maintaining internal coherence without energy exchange. Only when this homogeneous oscillation is disturbed does a local inertial response appear, expressed as a coupling to the surrounding space-time structure of the LEDO-field.
Consequently, changes in the propagation of an energy-density oscillation cannot occur instantaneously. They are constrained by the inertial response of the participating Rotons and by the angular tolerances required to preserve resonance coherence. The effective reaction speed emerges from this interplay and is further shaped by ambient background fluctuations of the LEDO-field. These fluctuations provide a probabilistic landscape in which rotating entities explore nearby configurations of improved energy-density balance.
While the LEDO-field itself oscillates as a global integral without spatial delay, coherent objects migrate only gradually through successive local reorientations. They settle into rotation axes and trajectories that preserve coherence while minimizing energetic tension with the surrounding field. In this manner, autonomous oscillatory structures follow natural energetic geodesics, provided their adjustments remain within the tolerance range set by the background LEDO fluctuations.
Static field = Resonance Potential field
In RQM, static electrical and gravitational fields represent the same underlying concept: a resonance potential field. Both describe the global availability of compatible resonance states between Rotons. Wherever coherent resonance compatibility exists, the corresponding potential is present immediately and without distance-dependent attenuation.
Entangled or resonance-coupled systems share this resonance agreement as a structural condition of the LEDO-field. Event-resonance potentials are therefore globally distributed. A static field does not arise from a propagating signal but from the existence of a realizable coupling. Electrical and gravitational fields are thus instantaneously available as resonance potentials. Consequently, a target is attracted toward a source at its actual current location, not at the historical position from which a photon may once have been emitted.
Predictions:
- Static electrical and gravitational forces reflect globally available resonance potentials and therefore always refer to the actual configuration of the source.
- Changes in these potentials generate propagating adjustments. These appear as photons (electromagnetic waves) and are limited by the characteristic propagation speed of such disturbances.
- Any change requiring photon exchange or field reconfiguration is subject to inertial coupling with the surrounding environment and cannot occur instantaneously.
- Internal adjustments of multi-rotational coherent objects can remain self-contained and periodic when confined within closed resonance cycles. Such internal reconfigurations remain inertial but may occur without radiative energy exchange if coherence is preserved.
This framework suggests that multi-rotational systems naturally converge toward fast periodic repetition of sub-rotations. By locking into closed resonance cycles, the object maintains coherence without requiring continuous photon-mediated adjustment. Energy dispersion through radiation becomes unnecessary as long as internal resonance compatibility is maintained.
The immediate availability of static attraction does not contradict relativity. Relativity constrains the propagation of changes in fields, not the existence of globally consistent field configurations. In RQM, static resonance potentials are structural properties of the LEDO-field, whereas photons represent carriers of discrete adjustments of these structures. The speed of light therefore characterizes the propagation of causal disturbances within the field, not the existence of resonance compatibility itself.
A constant, distance-independent availability of resonance-coupled attraction emerges as a necessity for coherent trajectories of interacting systems. Without such globally available potentials, stable motion under static fields would require continuous photon exchange and would lead to persistent radiative loss. The persistence of coherent, non-radiating trajectories thus reflects the presence of stable resonance potentials that do not require ongoing signal-mediated maintenance.
Global Resonance Agreement
The Resonance Coupling Field (IGT) establishes resonance channels through a global, a-temporal resonance agreement rather than through time-propagating interactions. It determines whether a resonance can exist as a consistent, fully realizable structure, independent of temporal ordering. This requires causality on undisturbed levels to be bi-temporal. Resonance existence is conditioned on mutual consistency between forward- and backward-temporal boundary conditions, similar to the ends of a violin string. The IGT therefore evaluates resonance compatibility across time as a whole, not along a directed timeline.
Bi-temporal causality is a direct consequence of global resonance agreement. Apparent retro-causal effects occur when future-compatible configurations participate in resonance consistency, not through backward signaling. If a system fails to realize the required future interaction, the resonance agreement never existed, and no information was exchanged across time.
Continuous perturbations that prevent backward-compatible boundary conditions suppress the formation of stable entangled resonances. Consequently, persistent global resonances are expected only in regimes of high temporal coherence, notably at quantum scales and possibly at cosmological scales. Extreme boundary conditions, such as event horizons, may relax these constraints and re-enable large-scale global resonance structures.
Inertia and Decoupling
Inertia decoupling↗
General Inertia↗
In the rotonal view, inertia can be interpreted as the time required for a system to realign its internal phases into a coherent configuration. During this interval, the system cannot fully sustain its external resonance channels and temporarily decouples from its surroundings.
A system is considered to be in a coherent state when its internal phase relations allow it to respond as a unified compound. In such a state, it maintains a stable center of energy density together with a continuous internal flow of energy density, enabling consistent coupling to external structures.
Coherence is therefore not an isolated property but a symmetric dynamical relation: systems with comparable coupling capacity mutually establish and maintain resonance channels only to the extent that each can preserve its internal phase alignment.
Radiation
In RQM, the standard use of the terms field and radiation refers to several distinct physical situations that share a common basis in resonance dynamics but differ in their realization.
- The presence of electrons establishes stable resonance potentials and constant couplings: a static electric field.
- The presence of higher-order rotonal systems establishes analogous resonance potentials: a static gravitational field.
- Inhomogeneous interaction of rotational systems, when they cannot follow their natural coherent trajectories, requires kinematic or energetic correction. This correction appears as the emission of a photon carrying energy and momentum.
- Photon emission corresponds to a propagating electromagnetic disturbance traveling linearly at speed $c$.
- The presence of photons establishes propagating resonance potentials that typically do not realize stable coupling conditions but remain transient carriers of adjustment.
Radiation therefore emerges whenever a rotational system must correct a deviation from its coherent resonance trajectory. A change of direction, phase relation, or rotational momentum requires redistribution of energy and angular balance. This redistribution cannot occur instantaneously within the object if coherence would be broken. Instead, the correction is emitted outward as a photon, preserving overall conservation of momentum and energy while allowing the emitting structure to settle into a new coherent configuration.
The term radiation thus describes the propagation of such corrections rather than the static presence of resonance potentials. Static fields correspond to continuously realizable resonance compatibility, whereas radiation reflects discrete adjustments required when coherence cannot be maintained locally.
Photons propagate at speed $begin:math:text$c$end:math:text$ because they represent the limiting case of a self-coherent propagating correction. Their internal phase relation is already fully satisfied for linear propagation, and they experience negligible inertial resistance from additional rotational degrees of freedom. As a result, no further internal adjustment is required to maintain their motion.
Photons generally do not interact strongly with one another because their phase-keeping condition is already fulfilled in free propagation. Without unmet resonance conditions, no corrective emission is required and no stable coupling is realized. Interaction can nevertheless occur through axis alignment or through mediation by other rotonal systems where resonance compatibility conditions become available.
Since photons already propagate at the maximal causal adjustment speed, they cannot naturally emit further photons to alter their own momentum without external coupling. Any change in their trajectory therefore requires interaction with a system possessing additional rotational degrees of freedom capable of absorbing or redistributing the corresponding correction.
Light
A photon represents the most elementary realization of a Roton, characterized by a single axis rotation. Its propagation at the speed of light follows directly from this structure: as long as its rotation axis remains unchanged, no inertial resistance to translation is imposed. In this sense, a photon propagates at maximal speed not because it is driven, but because nothing opposes its motion. At the same time, the photon tends to escape its own localized energy density, reinforcing this unrestricted propagation.
The apparent speed limit of light can be discussed from two complementary perspectives, both subordinate to this invariant.
First, even a nominally planar LEDO base-soliton possesses a minute orthogonal extent. If not inherent, background fluctuations inevitably introduce small transverse components. As a result, the photon’s self-induced acceleration via its own energy-density gradient is weakly constrained by its resonance characteristics and by ambient fluctuations. This does not reduce its speed, but slightly broadens the space of admissible motion.
Second, the model predicts residual coupling to the surrounding universe. Even an ideal planar Roton experiences axial resonance potentials from other photons that are accidentally aligned along similar oscillation axes. Although a photon’s phase is internally unrestricted and adapts instantaneously, transient virtual axis alignments still occur. These fluctuations largely cancel statistically, yet their integration requires finite response time governed by the Inertial Gyroscopic Tensor (IGT) field, inducing a minute precessional component. Preserving the relative rotation axis may therefore lead to subtle changes in propagation direction.
In this sense, a pure photon is a one-dimensional oscillation that would propagate without time dilation, but is weakly forced into an effectively two-dimensional motion, acquiring a vanishingly small rotational inertia. Consequently, the speed of light may depend weakly on the integrated background resonance fluctuations of a given region of the universe. Passing near heavy masses—composed of or containing many photon-like components—may therefore induce slight changes in a photon’s rotation axis and trajectory, without altering its local propagation speed.
Postulate: A photon is a basic Roton with a single one-dimensional oscillation, yet remains susceptible to minimal precession.
Takeaway: A photon may follow non-linear trajectories without loss of speed, provided its rotation axis remains unchanged.
Base Sonon
The base Sonon only requires a basis in space-time for its resonance. A resonance with a directional (vectorial) character. You can imagine it as a rotating positive and negative crest in a medium/field constantly falling into their crests rotating around itself. It’s amplitude and size potentially only limited by background fluctuations and LEDO dispersion.
Looking at potential characteristics of a base Sonon in the LEDO-landscape we’d rather have to ask about the size of it. As the LEDO-landscape only interacts with us via stable excitations (higher level roton) the size would not necessarily matter. So in the end it could either behave point-like (from its center) or need to be smaller than the observable interaction range of higher level rotons. But in context of the smallest kind of photons they could build up and taking its rotation radius into account we could basically come to a length which was already defined by planck as the planck constant:
$L \sim \sqrt{\frac{\hbar G}{c^3}}$ = Planck length (~1.6×10⁻³⁵ m)
Using the characteristic parameters: speed of light $c$, gravitational constant $G$, Planck constant $\hbar$
(TODO: Add definition of planck constant and from where it applies)
[Model-Remark: At this stage of the model, we might potentially change to the concept of a photon being a 1-Tier Di-Sonon and an Electron being a 3-Tier Sonon. From the fact, that both a Sonon and Electron show no fixed size into our space. Interaction of photons and electrons would then naturally emerge as the creation of a Sonon-pair induced by an IGT torque carrying the counter-momentum. After propagation of the inertial change down to the level of the electron, the electron can not further loose its inertial change than creating a Sonen/Anti-Sonon pair that instantly create a resonance-coupled Roton. The size of which is purely defined of the absorption energy. Starting from a distance of zero The Sonons will eventually find their perfect distance matching to the momentum. The photon carries away the exact difference in momentum - and yes you can think of it purely kinetically at that level.]
Energy dissipation on different levels
Does every change in rotonal properties lead to an emission of a photon? Not necessarily. The Roton might be able, to exchange the resonance change via other higher level resonance channels. Atoms for instance might already dissipate their energy-change via thermal resonance channel interaction increasing their Kinetic vibration via the inter atom resonance-channels. Keeping their Distance intact allows the system to contain more energy. So they attract each other (standard physics: gravitationally) but only the keep their distance optimal while increasing energy density. So is an electron in an atom attracted by the mass of the earth? No, the rotational trajectory is not changed into an ellipse if the subsystem is confined (all resonance channels fulfilled).
Photon Propagation and Interaction
Within the Rotonal Quantum Model (RQM), a photon is understood as the most elementary Roton: a single, one-axial oscillation whose identity is inseparable from propagation. This interpretation leads to some unified explanations:
Gravitational lensing: is the adiabatic precession of a photon’s rotation axis in an anisotropic resonance landscape.
Photon Rest frame: Photons do not interact by slowing down, but by reorienting how they may continue to move.
Time dilation: Time dilation does not apply to photons because there is no internal rotational sub-structure against which time could accumulate.
Photons propagate freely because their axis is preserved; they interact because their axis can reorient; they do not age because they have no internal resistance to phase evolution.
Axis Preservation and Gravitational Lensing
A photon propagates linearly at the speed of light as long as its rotation axis remains unchanged, encountering no inertial resistance to translation. Gravitational lensing is therefore not interpreted as the result of a force acting on the photon, but as a gradual precession of its rotation axis. Massive structures generate anisotropic resonance potentials summarized by the Inertial Gyroscopic Tensor (IGT) field. As a photon traverses such a region, its admissible propagation direction is continuously reoriented, producing smooth trajectory curvature without any change in speed or energy.
Absence of a Rest Frame and the Possibility of Interaction
A photon has no rest frame because its oscillatory state cannot be separated from its motion, once present it instantly accelerates. Nevertheless, photons interact through resonance coupling, not through rest-frame kinematics. Phase alignment, axis orientation, and transient resonance overlap allow photons to scatter, couple, and respond to external structures without requiring a rest frame or velocity change.
Why Time Dilation Does Not Apply to Photons
Time dilation measures resistance to change of internal state under motion. For a photon, no such independent internal clock exists: phase evolution and propagation are identical. Consequently, no proper state time accumulates along a photon’s trajectory. Only residual effects, such as minimal axis precession induced by background resonance fluctuations, introduce vanishingly small transverse inertia without generating time dilation.
Unified View
In the RQM framework:
- Speed invariance follows from preservation of the rotation axis.
- Interaction and lensing arise from slow reorientation of that axis within an anisotropic resonance landscape.
- The absence of time dilation reflects the lack of internal rotational structure against which time could accumulate.
A photon may therefore follow curved or non-linear trajectories without loss of speed, energy, or coherence, provided its fundamental single axis oscillatory character is preserved.
Standard physics and quantum theory read↗
You might be eager to know int terms of standard physics what the Roton model tells you about the world? This note tries to avoid as much of the roton model terms as possible.
Elementary Particles read↗
If multiple Rotons come closer and succeed to overcome their energy density pressure they build other stable compounds. In this way photons cluster to packets or start to enter 3D. Intuitively an electron might be a compound of 3 photons rotating in 3 different spatial directions (see Resonon). Even a single Photon might be bent into 3D world creating a stable self-resonant closed loop. Maybe it is also a combination of 3 Loops of electrons.
Postulate: An electron is a (elementary) particle built from photons oscillating in 3 dimensional trajectories around a common center. It can build entanglements into 3 spatial directions.
Compound Matter
Driven by the current energy density gradients and background fluctuations in the LEDO-Field the world constantly and inevitably “tries” to find optimal distributions of energy. Rotational electron-compounds start to create stable structures resisting the worlds tendency to entropy. Electrons build rotational pairs (e.g. as observed in atoms) that attract each other. Differently layered rotational electron-compounds start to create stable structures resisting the worlds tendency to entropy.
Spoiler: Electrons build up nuclei with the purpose to simply hold electrons at their place which attracts entangled electrons into its orbitals.
Object Tiers
There are different “Tiers” of Rotonal objects in the world. Depending on how many dimensions their resonance coupling enters.
- Tier 1 - Photon
- A Photon is the first tier/level of a single Roton object and is only locked in one single direction. It does not have any other rotating sub-structures which might extend into other dimensions. It has a single rotation axis with no (native) precession. It can therefore travel in linear direction in full speed with no imposed inertia, as it already has full speed and couples to nearly nothing during its travel. In addition, there is no inertia imposed by any rotational substructures. While interacting with matter a change of the rotation axis seems to take no time.
Postulate: A photon can travel along a curved trajectory, in case where this does not demand changes in its rotation axis = axis is orthogonal to the curve plane.
- Tier 2
- A Neutrino has two rotating axis (or a main-axis with some tilt). This allows it to travel (nearly) at the speed of light provided it can align to the current center of the rotonal force with both axis. So one axis orthogonal to the rotation plane through the attractive force. And the second trying to impose as less inertia to the second rotation ring as possible. Most likely into tangential direction. But there are not much Rotons in the mode of Neutrinos in the world to interact with anyway.
- Tier 3
- Electrons are built of 3 Level-1 Objects. 3 Rotating Roton-Pairs, one for each new dimension. The electron elementary particle is locked in place and therefore bound to it’s 3 rotation axes. It resists axis movement and as a consequence acceleration. Constantly moving into one direction is Ok. But acceleration is limited by the opposed rotational inertia of their axes. (Could it get flat?) Rotonal inertia holds it back from traveling faster than some coupling constant.

Time and Rotonal Inertia
Time: Time is the resistance of the universe to instant reorientation of a rotonal alignment. Photons experience no time as they could reorient themselves instantly when interacting with matter. The more contained rotonal energy a system has (rotonal inertia) the slower local time gets though (at least from the formulas). Example: Big masses, black holes.
Dark Matter read↗
Dark matter was introduced to name a yet unknown force, which modern physics still fails to find. Why? Because dark matter doesn’t exist. Modern physics expects it to be a gravitational force originating from matter. But it actually is a dark energy or rather a dark force. Modern physics has not yet realized that the rotations within a galaxy generates resonances and forces. These forces are missing in current calculations and account for a large portion of the attractive influences, which are mistakenly attributed to atomic-level phenomena like gravitation. According to the Roton model the missing attractive forces are actually caused by rotations at the galactic scale.

Atom Physics
We show an alternative Olavian Atom Model. It’s intuitive character is based on attractions of resonating Rotons. Depending on the environment, atoms take different structures and varying energy optima. The Olavian Atom orbitals are closed trajectories taking up the combined resonances of multiple base rotations. The p-orbitals or resonant couplings to s-orbitals of different sizes, e.g. p2 couples to the s1 and s2 shells.
Atom Orbital Model read↗
We first focus on the electron orbital representation of atoms. Atoms are an optimization of rotational energies to iteratively reach more energetically optimal rotations in respect to the Roton Model. The most attractive constellations are co-axially entangled (electron-proton-proton-electron) Roton coupling combinations. Furthermore electrons find their places in resonant distances from the center. Further optimizations allow electrons to lock into resonances with multiple other electrons with different rotation radii (a Resonon). An electrons planar Rotonal rotation can start to precess (tilt) to couple with electrons of different shells.
Finding: The standard physics term “excitation” (e.g. of a quark or electron) often translates well to temporal “precession” within the sub-roton states.

Why do bonds between atoms lead to stable molecules? Let’s understand the most attractive binding type and reveal that it is based on electron entanglement and electron trajectory resonances. Even electrons of different atoms can create “Entangled” pairs, while still keeping their entanglement to “their” own protons alive. This again leads to the most attractive bond between two electrons and two protons of different atoms. The radius of valence shells in a molecule are driven by this bonding - and are roughly equal between different elementary atoms.
The Electron read↗
The electron, one of the most fundamental particles in nature, remains among the least understood. We try to build an electron based on photons traveling on self-resonant loops. The master class, want to try yourself before jumping into the authors visionary proposal?
Insight: Electrons build entangled chains keeping their distance and speed in a common direction. For instance when passing along an atom lattice. The protons of the atoms are not expected to disturb them, as the free electrons do not have individual rotonal entanglements to the atom cores.
We will show how protons can be structured with Rotons such that we can describe the observed Electron-Proton attraction.
Insights: Leptons (Protons and electrons) are ‘cages’ that keep electrons stable in space and orientation. Such a cage shell is called Proton when it contains an electron locked in space and phase.
Nuclei (Proton, Neutrons, Alpha) read↗
The Nucleus of an atom consists of Protons and Neutrons, as they say. It has this task: Provide maximal attraction for the resonant orbital electron trajectories. So the proton or more precisely the co-electron in the nucleus needs special geometrical freedom to provide the rotating electron with the constant possibility to share their axis. The nucleus shows nearly symmetric compound-objects to hold lepton(s). A structure that confines the protons “charge” (co-axially anti-parallel to electron). This allows the entangled electrons location to rotate freely and remain entangled. completely independent of the other protons and neutrons on the nucleon. All nuclei contain one or two such Leptons.

We well see interesting predictions regarding the ratio of protons and electrons in different atoms and isotopes.
Alpha-Particle read↗
The atom core has to allow a full symmetric rotation of two orbital electrons. Paired electrons need a co-axial rotation around a central nucleus. This needs a linear Electron-“Proton”-“Proton”-Electron coupling. Each electron couples individually to its own proton. So the linear Proton-Proton object in the atom core needs to be able to freely rotate virtually in all spatial directions. A symmetric compound is needed to fulfills this task. A compound, which hosts 2 “charged” particles which can entangle with 2 orbital electrons.
Why shall a huge proton have the exact same charge as a point-like electron? Well, now you know: it does not. Protons, Nucleons and Alpha-Particles are only heavy containers which keep electrons/positrons in place so they can entangle with the free rotating electrons in the orbitals. A container which holds charges in place via energy density repulsion still allowing them to rotate within the Alpha-Particles shell.
The alpha-particle is not simply an energetically favorable state - as simply observed and proclaimed by standard physics. It serves a specific purpose. It is a pre-requisite to enable electron-pairs to rotate around their entangled nuclei. The Alpha-particle is a necessity and prediction of the Roton-model. Fortunately it has already been discovered, named and nearly seen as an own particle with high symmetry even in standard and quantum physics. But with no glimpse of what is shall be good for.
We proudly present an (outdated but nice) illustration of an Olavian version of the Alpha-Particle. We choose a symmetric constellation of 4 Nuclei with 4 Sonons (3 Quarks) and 2 Pole-Caps conveying the charge itself. The so called Alpha Particle is a special combination of 2 electrons or positrons (if you prefer) confined in a cage built of the Quons (quarks) from 2 Protons and 2 Neutrons (equal to 18-20 Inter-Resonant quons). This $\alpha$ particle is the predominant basic building block of atom nuclei.

The alpha-particle keeps the electrons in line and holds them together so they can keep a more stable distance and resonance. This allows to attract free electrons even closer.
The question also arises, why atoms seem to be built from Alpha-Particles - 2 Alpha-Particles use more space then 4 Deuterium-Cores. Answer: Because an $\Alpha$ two internal charges (e+) can rotate freely, and 2 rotating Deuterium-Cores use more space - if they could ever rotate as fast around themselves.
Only one single unpaired valence-electron will entangle to single proton, deuterium or tritium nuclei. So stable atom cores are not expected to have more than one isolated proton P or deuterium D nucleus.
Alpha Simulations
In simulations we modeled N-Tier Rotons as Gridons together with some rotonal resonance coupling. After a longer time of trying to adjust number of nodes, starting energies, resonance-lengths, channel-counts it was possible to show, that the chosen structures for nucleus actually emerged as stable objects. Have fun watching some videos.

Nucleus Scattering read↗
This chapter is to simulate what happens if you throw an electron at a nucleus. Result: Well, you need to aim really good, otherwise it simply flies through.
Isotope Challenge read↗
This chapter is to prove, that the Olavian Atom model can predict or at least explain the stable and unstable isotopes.
Quantum physics
Quantum Entanglement
We will demonstrate that quantum entanglement — particularly of photons and electrons — is a crucial factor in explaining why atomic nuclei hold together, and specifically why protons and electrons attract each other within atoms. To further explain certain phenomena with long-distance entanglement, we introduce the concept of bitemporal causality read↗: quanta are entangled because they always have been and ever will be entangled (within their lifespan). Both entangled twins share and remember their bi-directional future and past.

Measurability
For something to be observable by humans, it must interact with something humans can detect — such as light. This holds at least in the scales at which light can interact with Rotons the span of our atoms. However, on the scale of quarks and electrons, there is very little left which can be used to observe. We do not have anything even smaller to throw around. Observation always involves interaction. On this scale, every interaction destroys some of the original state. Thus, we can never measure the full state but only a statistical effect over many different measurements. This might lead to the conclusion that the even smaller components no longer interact with us directly. So we will never be able to directly “observe” any substructures. Still we can hope for the ability to trigger lower-level rotons to react via rotonal resistance (inertia) by manipulating and observing minimal state changes of higher level rotons and their coupling.
Decoherence (Collapse)
Decoherence of an entanglement denotes the breakdown of resonance alignment. Decoherence corresponds to the loss of phase-locked resonance channels due to uncontrolled coupling to external degrees of freedom. If a measurement or rather de-coupling is done on an entangled or hierarchical quantum, the full entanglement is destroyed. This might also mean, that these two quanta were never — and will never be — fully entangled. Two rotating entities with the exact same mode on a common rotation axis will be and remain entangled, due to increased resonances in axial direction. With this entanglement, small disturbances in orientation might even be stabilized. The entanglement breaks up if one quantum is forced out of its stable rotation axis strong enough. From this point on, entanglement will vanish, if the disturbance was too high. A disturbance on one of the entangled twins, might lead to a similar disturbance in the other twin. This is mainly the outside view of an underlying necessity for the bi-temporal character of a realized resonance entanglement. The resonance is not mainly an oscillation in space but also in time. Imagine a resonating violin string to be instantly made static - it wont. So whenever it is static in the future it will start to get static earlier on.
Background fluctuations
Energy density optimization in the LEDO landscape is driven by its stochastic background fluctuations on different spans.
Dynamics of Energy-Density read↗
Physical systems continuously seek states of maximally phase-coherent energy density across all coupled scales. Any acceleration, structural change, or environmental gradient temporarily dilutes this coherence, forcing energy into internal re-organization before optimal density can be restored. The time required for this re-synchronization manifests as inertia, while its rate defines the local flow of time. Gravitation and relativistic effects emerge naturally as regions where energy density must constantly re-optimize within strained resonance conditions. … continue↗
Time is not a fixed dimension through which systems move, but the rate at which coherent energy-density states are successfully re-established.
Inertia is not a fundamental resistance of matter, but the persistence of energy trapped in non-optimal configurations during re-synchronization.
Space is not an empty container, but the effective room required for energy-density distributions to regain phase coherence.
Gravitation is not a force acting at distance, but the signature of sustained energy-density re-optimization within coupled resonance gradients.
Time as we perceive it in our macroscopic view, is not an independently flowing universal background. It is fundamentally defined by the oscillatory periods and phase relations of coupled energy-density structures such as electrons, photons, and their higher-order resonant compounds. What we call time emerges from the stability, count, and mutual coherence of these oscillations across interacting systems.
If, for any reason, the oscillatory period of an electron or photon shifts relative to surrounding structures, then its local sequence of states progresses differently. A slower effective oscillation corresponds to a slower progression of physical processes when compared to a distant reference system. In such a case, an unstable particle decays more slowly, a chemical reaction proceeds more slowly, and an object ages more slowly relative to an external observer. From within the system itself, however, all internal processes remain consistent, since all coupled oscillators adjust together. Time therefore cannot be regarded as globally uniform; it is inherently local and relational.
Within the RQM framework, no universal background time is assumed. Instead, physical reality is built upon locally defined oscillatory periods, their harmonic relations, and their phase coupling across multiple scales. What is measured as time corresponds to the count and coherence of these oscillatory cycles within a given environment. Temporal flow is thus a property of resonant systems maintaining phase alignment rather than motion through a pre-existing temporal dimension.
Where general relativity describes gravitational environments as curvature of space-time, RQM interprets the same observations as the consequence of phase de-coherence and re-synchronization within coupled resonance structures. Strong gradients and persistent accelerations disturb optimal phase alignment, requiring continuous internal re-optimization of energy density. This ongoing adjustment slows the effective progression of coherent oscillatory cycles and therefore reduces the locally measured rate of time. In this view, gravitational time dilation reflects not a geometric warping of time itself, but the energetic cost of maintaining phase coherence within a dynamically strained resonance field.
Space may be understood as the resolution mechanism of resonant systems confronted with phase mismatch. Read on↗ offers a more narrative exploration of this idea. In brief, space persists because not all systems can remain in complete harmonic alignment. Were perfect coherence universally attainable, the universe would long since have converged into a single global resonance. Instead, persistent mismatches generate separation, while locally stable extrema form coherent structures that prevent total harmonic collapse. Space thus appears as the dynamic consequence of incomplete resonance and the stabilization of many local equilibria within an otherwise unifying tendency.
Space marks the distance between systems that cannot yet resonate as one.

Spacetime Curvature
In Einsteins words “Geometry tells matter how to move”. But what tells geometry how to be, and why is spacetime not negatively curved where no big masses are?
Instead of making “spacetime curve” we say that “resonance-density gradients shape effective geometry”. The apparent size of the universe could reflect how much global coherence is missing. So empty regions behave as if space expands outward.
In this view, space does not curve around mass but emerges wherever systems fail to establish coherent resonance. Stable structures such as stars and galaxies form local resonance minima that draw surrounding dynamics into partial alignment, producing converging trajectories that appear as gravitational curvature. Yet regions lacking such coherent anchoring expand or remain extended, as no common phase relation constrains them. Space therefore reflects the unresolved portion of universal resonance rather than a fixed geometric background. Distances grow where coherence cannot be established and contract where stable resonance persists, suggesting that the apparent size and curvature of the universe may be a measure of its incomplete harmonic integration.
Gravity
:tendency toward coherent phase alignment
Space
:measure of unresolved phase difference
Size
A photon may carry essentially any wavelength and energy, yet electrons and atoms appear only within a narrow and well-defined spatial scale. Their characteristic size is not arbitrary, nor obviously tied to a single local parameter. Why should an electron, a proton, or even a quark possess precisely the spatial and energetic extent we observe?
In the rotonal view, the basic atomic and subatomic particles adopt their characteristic size because stable particles of a given type converge toward a common resonance scale. This alignment is not imposed locally but emerges from the oscillatory structure of the universal LEDO field. Within this background, it becomes energetically favorable for similar particles to occupy comparable spatial and energetic configurations, as only such alignment permits persistent and coherent coupling. Particle size therefore reflects global resonance compatibility rather than an isolated intrinsic parameter, with individual systems stabilizing where their internal dynamics best match the prevailing resonance environment.
The characteristic size of atoms is thus not determined solely by their internal Coulomb balance, but also by the requirement to maintain coherent resonance with the surrounding resonance potential field. Each element possesses its own internal structure of attractive and repulsive energy-density flows, yet stable atomic systems tend to contract or expand until their outer electron span remains compatible with the prevailing resonance scale. This leads to a narrow band of preferred atomic radii across otherwise very different elements such as Mg or Rn. Internal structure determines how efficiently this adjustment can be achieved, but the target range itself reflects an external coherence condition rather than a purely local equilibrium.
At first glance this may appear almost trivial: identical internal structures yield identical energies and therefore identical spatial extensions. Yet the picture becomes more subtle when one considers that the outermost paired-electron orbitals of most atoms occupy a remarkably narrow radial band of roughly 0.5–2.2 Å. Such uniformity across very different elements suggests that orbital shells may not be determined purely from internal structure alone. Instead, electron distributions may first settle into spatial ranges that remain compatible with the prevailing external resonance environment, and only then resolve inward according to the specific internal configuration of the atom. Atomic size thus emerges from a continuous optimization between internal energy-density dynamics and global resonance compatibility.
Antimatter asymmetry
The observed dominance of matter over antimatter suggests that creation processes in the early universe were not perfectly symmetric. Any viable model must therefore include mechanisms that introduce directional or phase asymmetries during formation, allowing one class of stable resonance structures to dominate over its mirror counterpart. In this framework, the observed predominance of matter can be interpreted as the consequence of an early arbitrary symmetry selection within the resonance field. Once a preferred rotational or phase orientation becomes locally established, subsequent creation processes no longer occur in a neutral background but within an already biased resonance environment.
Locality
Having said that reminds us about how to measure length. So if the basis of length is the size of e.g. a hydrogen atom, then yes, atoms have the same size in the whole universe. If the basis for length though is time (e.g. speed of light c) which is distance during a given time which again is a rotation duration of an electron in space well … I’d go with the egg not the chicken. If you define and measure the width of an electron by the circumference of an electron (time), well then all electrons have the same size - everywhere. So physics can actually not necessarily force neither local time nor local space to be uniform, linear or comparable in the whole universe.

Rotating entities create a directed resonance potential at which span (size, frequency) they can couple into the universal resonance-field. This will be described as inertia.
On basis of the Roton model, Inertia would be: resistance of a body to acceleration induced by another body. Or more precisely the resistance to change of rotation axis induced by LEDO-field resonances. Overall it is the sum of all energy placement, rotational attributes, attractions and temporal changes thereof between the two objects. And this all in a dynamic self-looped context. This might imply though, that a body has no universal inertia, but an inertia that depends on the source object. Acceleration depends on the sub-structure and sub-behavior of both objects. So the “weight” of the atoms listed in the periodic system might depend on the atomic composition of (e.g.) the earth. So in the optimal case, you as a reader already have a few experiments in mind to disprove this concept - maybe measure atoms on the moon?
Think of a Roton as a spring along its diametrical span. If a force starts to drag on one Sub-Particle, this will lead to some tension in the spring in either direction. Leading to squeezing, wobbling and precession of the rotonal path. This tension remains as long as the force applies. So any change of direction or force leads to a counter-force between the Twin and Twon roton. A force on the level of an atom span (gravity) will initially only influence the atom-span roton. But if that force changes, the Sub-Rotons need to adjust too. So they react on the first-derivative of the applied force (force change). This can be propagated downwards to the even smaller Sub-Rotons. In addition, this is also propagated upwards to the environment in the form of further resonances or temperature effects. The higher level environment reacts on it as an integral over the sub-states (e.g. as in a microwave oven).
Cosmic structures
Galaxies when modeled as Rotons build stable flowing and pulsing structures. These are also known as filaments.

Galactic filaments can be interpreted as large-scale resonance links connecting temporal nodes within a bi-temporal framework. Their coherence reflects global resonance agreement rather than sustained causal transport. Only matter configurations compatible with both past formation and future evolution persist as filamentary structures, while incompatible trajectories fail to establish or maintain coherence.
This indicates, that the universe as a whole reaches for long-term stable structures, otherwise it would simply not exist.
Size of an atom - cosmic oscillations read↗
Why does an atom have the size it has today? And why do atoms take stable orbitals at the distance they have today? This is caused by a background fluctuation which have some maximum resonances in the spatial size of atoms. This LEDO-Field fluctuation on atom level can actually be confirmed indirectly via a measurable uniform radiation, originating from objects from an earlier time in the universe. Evidence comes from the existence of a cosmic microwave background (CMB) read↗ matching to the radiation emitted by objects the size magnitude of an atom.

Voids as the Dominant Optical Medium
Gravitational lensing is usually attributed to mass: stars and galaxies bend light inward and focus it. Yet on cosmic scales most of the universe consists of vast voids, not dense structures. These regions contain far less matter than average and therefore act as weak diverging lenses. Light passing through them spreads slightly outward, producing subtle de-magnification and shear that can be measured statistically across large sky surveys.
The universe thus behaves as a network of both lenses and anti-lenses, with light continuously guided by gradients of structure across immense distances. Interpreted more broadly, massive systems may represent regions of strong local coherence that draw trajectories inward, while voids mark regions where such coherence is absent and paths naturally diverge. In this sense, the large-scale geometry of the cosmos may be shaped as much by its vast regions of low coherence as by the structures that condense within it.
In the rotonal view, matter represents persistent local disturbances within the universal resonance coherence, structures that maintain their identity by continuously negotiating phase mismatch with their surroundings. Around such enduring resonance knots, additional “space” is required to accommodate incomplete alignment, and trajectories curve toward these stable centers. Vast voids, by contrast, contain little that resists global coherence. With fewer persistent mismatches to sustain separation, the need for extended spatial buffering diminishes, and effective trajectories gently diverge as the background approaches a more uniform phase condition. In this sense, matter marks regions where coherence cannot fully settle, while voids reveal where the universe comes closest to its undisturbed harmonic state.
Black holes and spacetime curvature read↗
Big masses lead photons into curved paths. Instead of bending space and time to explain this effect, the Roton-Model explains this quite naturally with residual attractive resonances. These lead to a slow-down of rotational periods of objects. Even though a photons rotation is purely planar, random background fluctuations still expose it to minimal inertia. Is there any place where field fluctuations cease entirely? You could imagine the infinity of the universe being like the singularity of a black hole, inverted and point-mirrored. The closer you get the slower you become, atomar processes slow down, time starts to pass slower and slower. You will never reach the center or in this case infinity. The fade out of fluctuations and asymmetric alignment of resonance potentials at this rotonal scale prevents any further motion. The universe is the final Roton caught in self-resonance, from where nothing will ever escape.
Block holes might be objects that re-opening bi-temporal causality to galactical scales. The sever causal accessibility while preserving global consistency. A black hole does not transport information forward in time, but enforces consistency across time. This makes it a natural anchor point for backward-compatible resonance structures. In this sense, Galaxies do not fall into black holes because they are attracted. They remain because incompatible futures quietly cancel themselves out. A black hole does not amplify nor return resonances.
It silences time, until only globally consistent modes remain. In bi-temporal causality, the universe does not correct itself. It simply refuses to realize inconsistent histories.
Black holes may function as bi-temporal boundary structures, suppressing local decoherence and enabling global resonance agreement across cosmological scales. In this view, large-scale coherence phenomena such as galactic filaments are not dynamically enforced but selectively permitted: only matter configurations compatible with both past formation and future consistency persist. No information is exchanged across time; instead, incompatible trajectories fail to establish resonance existence. Black holes thus act not as causal engines, but as temporal silencers, allowing only globally consistent modes of structure to remain.
A “temporal node” in a resonance network is a system which participates in resonance agreement across time, not along time. A “Temporal node” strongly suppresses accessible microstates, reduces effective temporal degrees of freedom and enforces boundary conditions across time. Or in other words, if you reverse time at a black hole, a galaxy could pop out as a whole and this would not contradict causality.

About Life, the Universe, and Everything
From what you have read so far, you will surely agree, that the universe starting from tiny oscillations up to its whole structure reaches out for a long-term stable structure, otherwise it would simply not exist.
With all these teasers, you are invited to dive into the details presented on this website as the “Roton Quantum Model” to see how easily this model explains complex behavior — even in areas where modern standard physics has yet to provide answers.
Yours, Olav le Doigt
Glossary read↗





























